IDOC or Intermediate Documents are commonly used in
case of data migration between SAP systems or between SAP and legacy
system or vice versa.This blog details the steps involved in configuring
a new IDOC and also list’s down the various transactions that are used
while working with IDOCs.
IDOCs can be classified into two . Inbound IDOCs and Outbound IDOCs.
Inbound IDOC : These are IDOCs which get the data into SAP system from external source i.e PI system or any other external system.
Outbound IDOC: These are IDOCs which are sent out from SAP system to any other system. i.e PI system or any other external system.
Important Tcodes in IDOC:
SALE - ALE menu
SM59 - To create RFC destination
WE21 - To create a port for destination
WE20 - Partner Profile
BD64 - Create a model view distribution
WE19 - Test tool for IDOC Processing
WE09/WE10 - IDOC business content
BD87 - to reprocess the error
WE02 - to view the list of idoc documents
BD20 - Inbound processing of IDOC
Reference Document: IDOC Basics for Functional consultant
SAP Reference: ALE document
Step 1 : We need to check the RFC
connections to the target system , it can be PI system or any external
system. If it is to a PI system then we need to check the connection
under ABAP connections in SM59 transaction and for external system under HTTP Connections to External System.
IDOCs can be classified into two . Inbound IDOCs and Outbound IDOCs.
Inbound IDOC : These are IDOCs which get the data into SAP system from external source i.e PI system or any other external system.
Outbound IDOC: These are IDOCs which are sent out from SAP system to any other system. i.e PI system or any other external system.
Important Tcodes in IDOC:
SALE - ALE menu
SM59 - To create RFC destination
WE21 - To create a port for destination
WE20 - Partner Profile
BD64 - Create a model view distribution
WE19 - Test tool for IDOC Processing
WE09/WE10 - IDOC business content
BD87 - to reprocess the error
WE02 - to view the list of idoc documents
BD20 - Inbound processing of IDOC
Reference Document: IDOC Basics for Functional consultant
SAP Reference: ALE document
Source Client - 300
Destination Client - 100
Logical System name and RFC destination name should be same.
Step 2: Create a port in both systems (Source & Destination) using transaction WE21
Step 3 : In transaction BD64, create a model view and create the message type details .
Specify the source client , destination client and message type details.
Step 4 : Go to More -> Environment -> Generate Partner profile and enter the model view name and execute the program
Do the same steps in both the client.
Click on Distribute the model view.
Verify the Partner Profile using the transaction code WE20
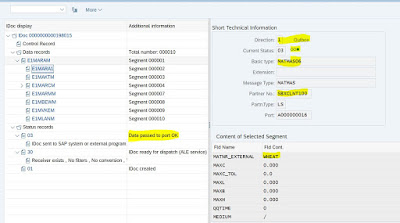
Step 5 : Send the outbound IDOC in Client 300, using Tcode : BD10 . Execute
Message Type : MATMAS (Material Detail) to SBXCLNT100 (Destination client)
Material Code : WHEAT
Step 6: To check the IDOC status using Tcode : WE02

Step 7 : Receive the Inbound IDOC in Client 100 using the Tcode: BD11
Message Type : MATMAS (Material Detail)
Material Code : WHEAT
On Destination system
- Goto WE20
- Locate the sender logical system (partner)
- In Inbound grid select message type MATMAS (double click)
- Change "Process code" AFSA to MATM (probably AFSA is the actual code)
- Save and reprocess the IDocs using BD87
Note: Process code AFSA is default but the scenarios need a specific code that is MATM














No comments:
Post a Comment